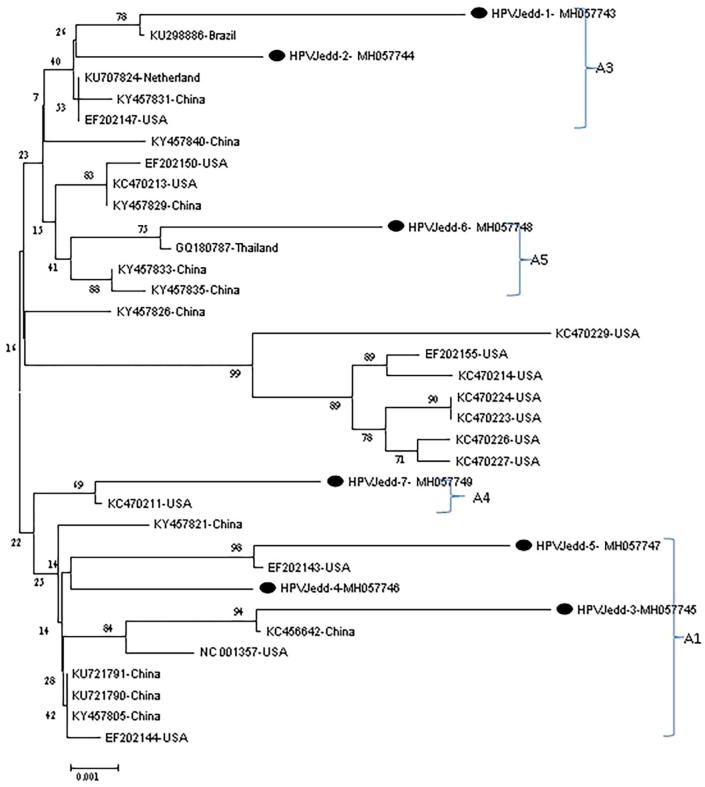
Alinity m HR HPV is a novel human papillomavirus (HPV) assay that individually identifies genotypes HPV16, HPV18 and HPV45, whereas reporting 11 different high-risk HPV (hrHPV) genotypes in two aggregates: HPV31/33/52/58 and HPV35/39/51/56/59/66/68.
The medical efficiency of Alinity for screening of cervical most cancers was evaluated in population-based settings. For ladies aged ≥30 years, the medical sensitivity (n=68) and specificity (n=3,077) to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2+ (CIN2+) of Alinity was 100.0% and 92.4%, respectively, and never inferior to that of Hybrid Capture 2 (hc2) (p=0.0006 and p<0.0001, respectively).
The intralaboratory reproducibility and interlaboratory settlement of Alinity had been 96.7% (kappa, 0.92) and 98.7% (kappa, 0.97), respectively. In the ≥30 years age group, ladies who had been baseline hrHPV-negative had decrease threat for CIN2+ at Three years utilizing Alinity (0.04%) versus these with regular baseline cytology (0.65%) and comparable threat to that of RealTime (0.04%), hc2 (0.08%) or cobas 4800 HPV (0.04%). HPV16/18 hrHPV an infection was related to a considerably increased baseline and 3-year CIN2+ and CIN3+ threat versus absence of HPV16/18 or presence of hrHPVs at baseline (all p values <0.05).
The baseline CIN2+ threat was 8.8% for HPV31/33/52/58 and a pair of.5% for HPV35/39/51/56/59/66/68, whereas the 3-year CIN2+ threat was 17.0% and 4.9%, respectively (relative threat 3.4 [p=0.03] and three.5 [p=0.003]), suggesting that prolonged genotyping of Alinity could also be priceless in bettering affected person threat stratification.
Alinity fulfils worldwide consensus guideline criteria for main cervical most cancers screening and will be thought-about as clinically validated, demonstrating comparable security to different clinically validated HPV checks.
Methylation estimates the danger of precancer in HPV-infected ladies with discrepant outcomes between cytology and HPV16/18 genotyping
Vigilant administration of ladies with high-risk humanpapillomavirus (hrHPV) is important in most cancers screening applications.
To this finish, we evaluated the efficiency of S5 (concentrating on DNA methylation in HPV16, HPV18, HPV31, HPV33, and human gene EPB41L3) to foretell cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or increased (CIN2+) in a pattern of hrHPV-infected ladies referred to colposcopy within the FRIDA Study, a big screening trial in Mexico.
A nested case-control pattern with ladies referred to colposcopy both by atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance or increased (ASCUS+) in cytology and/or optimistic for HPV sorts 16 or 18 was examined by S5. Seventy-nine instances of CIN2+ had been age-matched to 237 controls and not using a prognosis of CIN2+ (<CIN2). DNA from exfoliated cervical cells was bisulfite transformed and PCR amplified for S5 targets, and methylation was quantified at particular cytosines by pyrosequencing.
The S5 classifier separated ladies with CIN2+ from <CIN2 with a extremely vital space below the curve (AUC) of 0.75 (95% CI 0.69-0.82), whereas AUC for CIN3+ was 0.81 (95% CI 0.74-0.89). To optimize sensitivity and specificity for Mexico, an alternate S5 cutoff of three.7 was carried out to account for total increased methylation seen in our already triaged ladies.
All three invasive cancers had been detected by methylation or HPV16/18 however none by cytology. Sensitivity of S5 for CIN2+ was 62% (95% CI 50.4-72.7%), specificity was 73% (95% CI 66.9-78.5%), and adjusted PPV was 15.1% (95% CI 12.0-18.3%). In distinction, the crude sensitivity of HPV16/18 detection and cytology had been 63.3% (95% CI 51.7-73.9%) and 57.0% (95% CI 45.3-68.1%) respectively; specificity was 29.1% (95% CI 23.4-35.3%) and 62.4% (95% CI 55.9-68.6%) respectively, whereas adjusted PPV was 6.4% (95% CI 4.9-8.1%) and 10.5% (95% CI 8.0-13.1%), respectively.
Methylation testing might cut back colposcopy referrals by 30 to 50% with nearly no lack of sensitivity for CIN2+ and CIN3+.S5 testing on hrHPV-positive ladies considerably elevated diagnostic info in comparison with triage by HPV16/18 plus cytology and seems to have medical utility as an extra test to considerably reduce burdens on colposcopy.The FRIDA Study is registered in ClinicalTrials.gov , quantity NCT02510027.
The HumanPapillomavirus (HPV) E1 protein is the one viral protein with enzymatic exercise. The primary recognized perform of this protein is the regulation of the viral DNA replication.
Nevertheless, it has been demonstrated that the ablation of HPV18 E1 mRNA in HeLa cells promotes a deregulation of a number of genes, significantly these concerned in host protection mechanisms towards viral infections; nonetheless, the precise contribution of E1 protein in HPV-independent context has not been studied.
The intention of this work was to find out the impact of the HPV E1 protein within the regulation of mobile gene expression profiles evaluated via RNA-seq.
We discovered that E1 proteins from HPV16 and 18 induced an overexpression of various set of genes related to proliferation and differentiation processes, in addition to downregulation of immune response genes, together with IFNβ1 and IFNλ1 and Interferon-stimulated gene (ISG), that are necessary parts concerned within the antiviral immune response.
Together, our outcomes point out that HR-(High-Risk) and LR-(Low-Risk) HPV E1 proteins play an necessary function in inhibiting the anti-viral immune response.
E6/E7 and E6* From HPV16 and HPV18 Upregulate IL-6 Expression Independently of p53 in Keratinocytes
Keratinocyte an infection with high-risk humanpapillomavirus genotypes has been linked to most cancers growth. In cervix, the alpha HPV16 and HPV18 have been reported because the mayor causative brokers of cervical most cancers.
Oncogenic development and power irritation are carefully associated processes, with IL-6 as one of many primary pro-inflammatory cytokines concerned. However, there are restricted research in regards to the regulation of IL-6 by high and low threat HPVs and the HPV proteins implicated on this modulation.
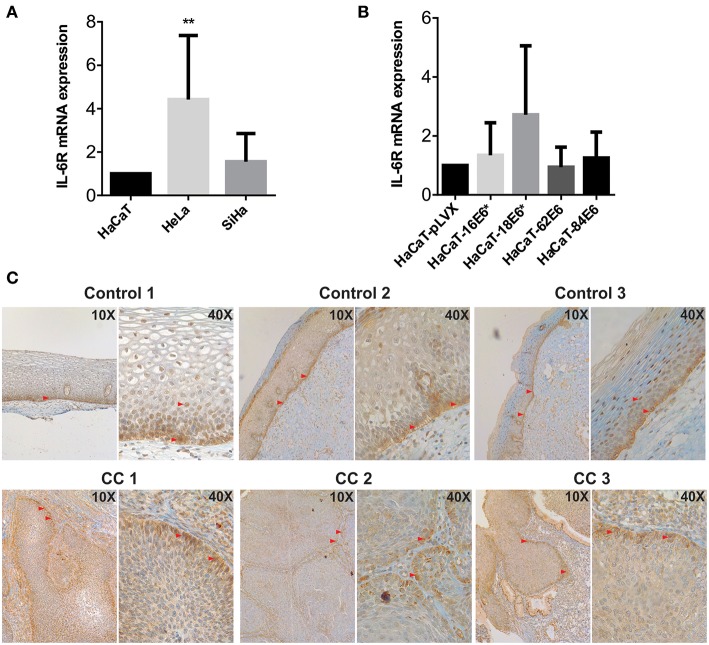
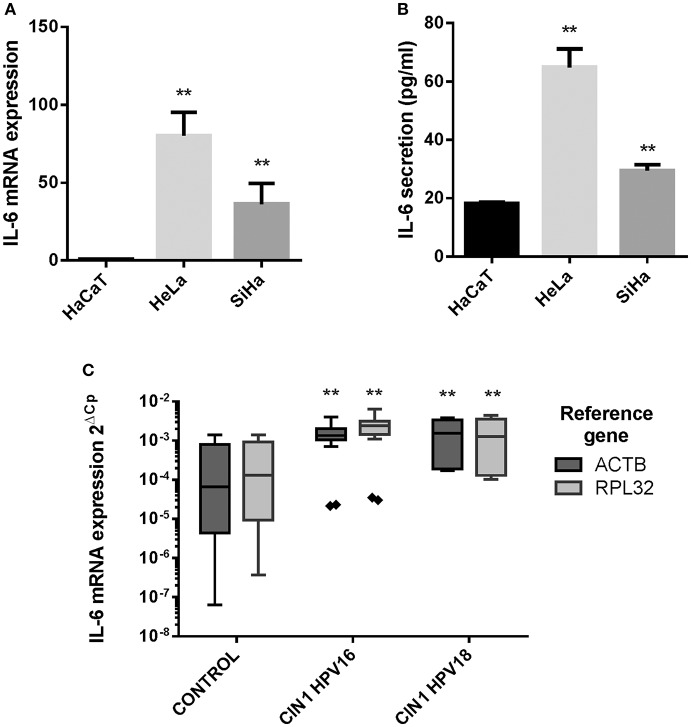
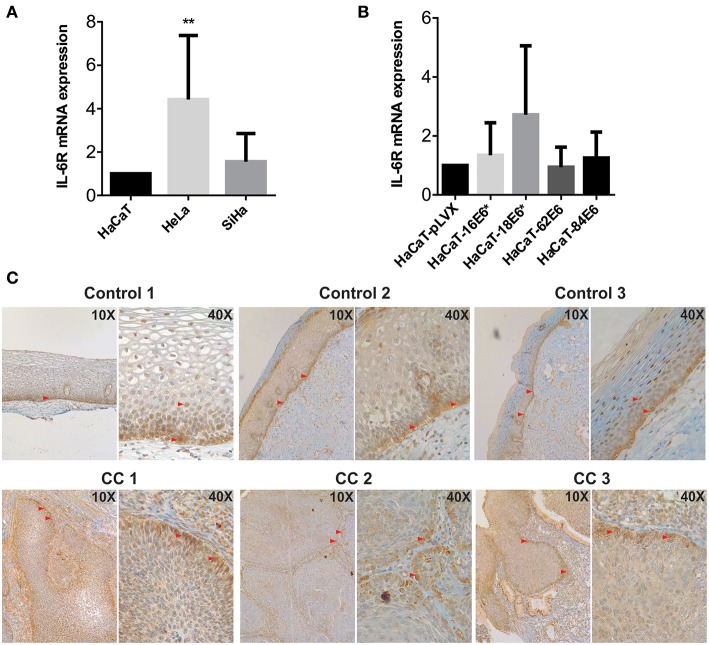
In this work, we report the overexpression of IL-6 in HPV contaminated cervical most cancers derived cell strains (HeLa and SiHa) in comparison with non-tumorigenic keratinocytes (HaCaT), and in Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia grade 1 HPV16 and HPV18 optimistic cervical samples in comparison with HPV adverse samples with out lesions.
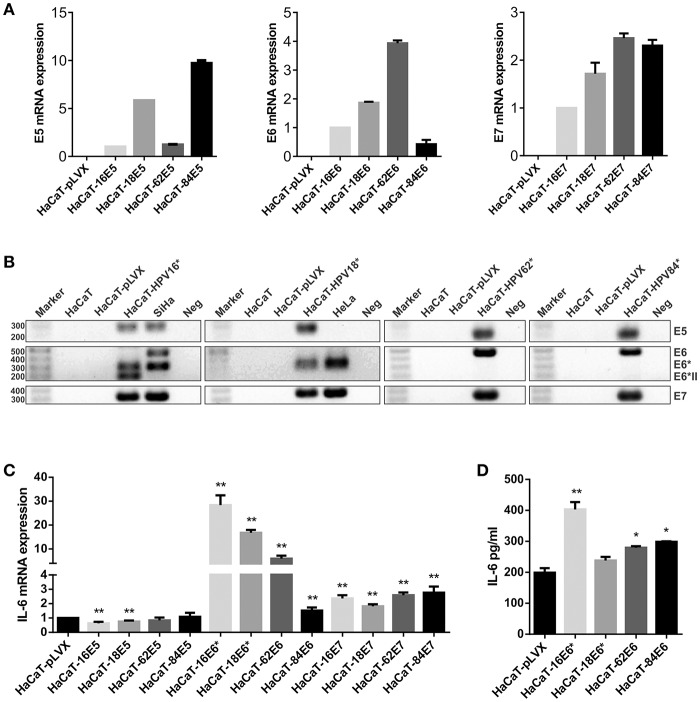
Moreover, we generated HaCaT keratinocytes that specific E5, E6, and E7 from excessive threat (16 or 18) or low threat (62 and 84) HPVs. E5 proteins don’t modify IL-6 expression, whereas E7 modestly improve it. Interestingly, E6 proteins in HaCaT cells upregulate IL-6 mRNA expression and protein secretion.
Indeed, in HaCaT cells that specific excessive threat HPV16E6 or HPV18E6 proteins, solely the truncated E6* isoforms had been expressed, exhibiting the stronger IL-6 overexpression, whereas in HaCaT cells that specific low threat HPV62 and HPV84 full size E6 proteins, IL-6 was additionally upregulated however not so drastically.
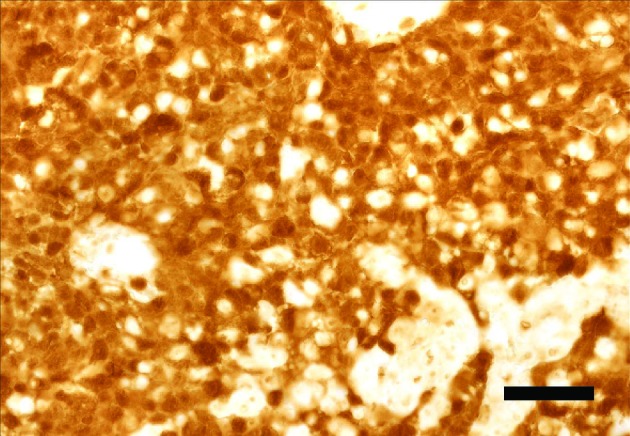
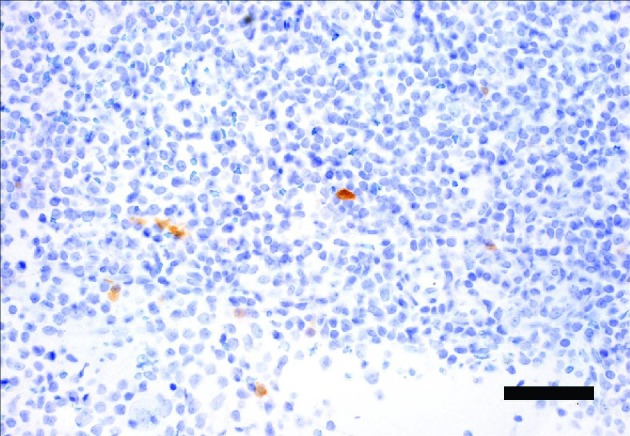
Since HaCaT cells have a mutated p53 kind that isn’t degraded by the introduction of E6 or E6/E7, it appears that evidently E6/E7 regulate IL-6 by an extra mechanism impartial of p53. In addition, basal keratinocytes confirmed a powerful expression of IL-6R utilizing immunohistochemistry, suggesting an autocrine mechanism over proliferative cells.
Altogether, IL-6 cytokine expression in keratinocytes is upregulated by E6 and E7 proteins from HPVs 16, 18, 62, and 84, particularly by excessive threat HPV16 and HPV18 E6*, which can contribute to advertise a pro-inflammatory and extremely proliferative microenvironment that may persist over time and result in cervical tumorigenesis.